Polling all colleagues and friends! Calling you here to serve up the results of the questionnaire you so kindly responded to about the one, nay—the many, data-slayer: artificial intelligence (AI). (And even more specifically generative AI.)
Impetus
The original impetus for this poll was a panel that I participated in at the Healthcare Internet Conference, first week of November. I knew that I was not particularly enamored of current generative AI tools, so I sought input from the many, whose opinions are often a better representation of the public-at-large rather than my own editor-at-medium professions (as in -sions that were professed).*
I also needed input as most of my own job functions are not those that AI comes in particular use for, but more about that later. Let’s break down the deets.
NOTE: Unless stated otherwise, this blog was written purely by—me—Jennifer Brass Jenkins, and is owned by—me—Jennifer Brass Jenkins. Be assured, however, that no AI was harmed in the making of it.
Questions, Answers, Predictions, & Hypotheses
The poll consisted of 10 questions (I didn’t realize how nicely that number came out). Some Qs asked for more clarity, some asked for demographic information, and most asked for open-ended answers, in order to tap y’all’s hidden genius.
Out of about 80 recipients, I received 39 responses. (YAASSS–WAY TO SHOW UP FOR THE TEAM Y’ALL!!) Though not all answers were required and thus answered by all respondents, all questions had at least 30 respondents.
The first questions were basic:
- Do you use AI in your work?
- If so, how often?
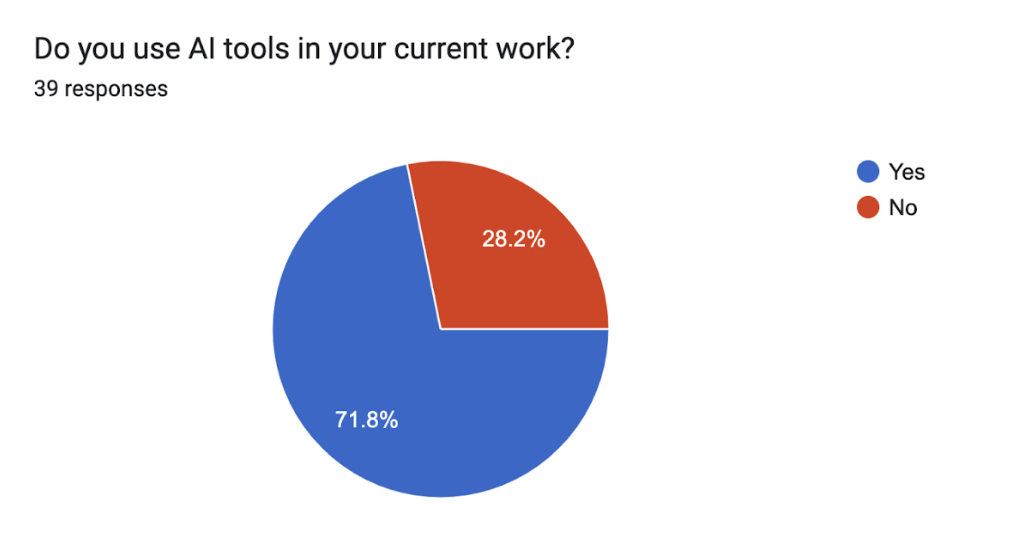
Fig 1: Pie chart showing the percentage of users who use AI tools in their current work (71.8%) vs. those who do not (28.2%).
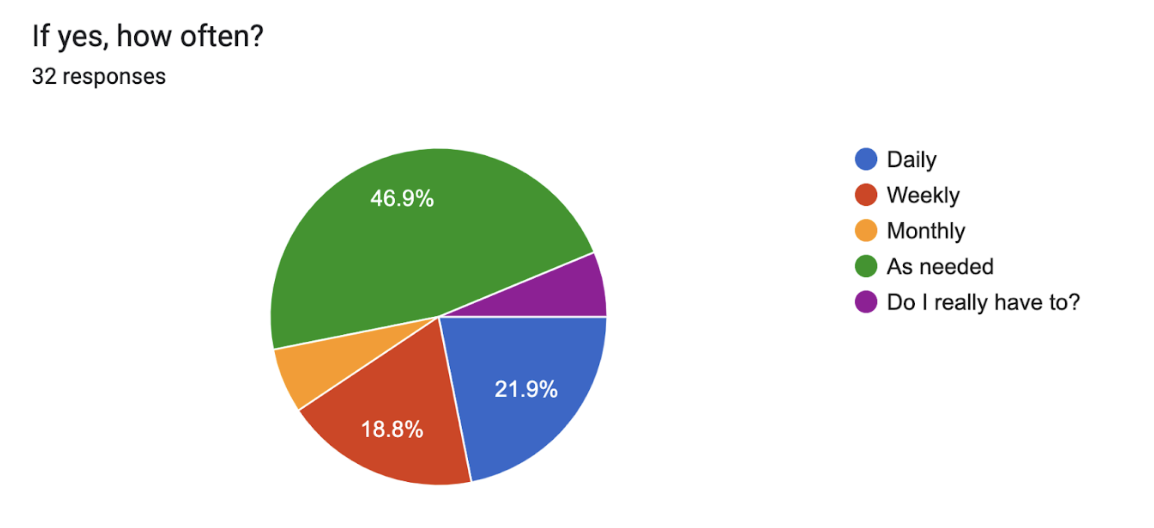
Fig 2: Pie chart showing how often those who use generative AI apply it with answer choices of daily, weekly, monthly, as needed, and a must-I option. (Note that two people chose “Do I really have to?”, which was one of my favorite answers.)
Out of the 39, 72% said they use generative AI in their current work. Of those, 18.8% said they use it daily. I’mma’ go out on a limb here and say that I think our web developers probably use it the most, aka daily.
Read this pithy commentary by our lead developer on how he uses and values AI. (TL;DR: He loves it and uses it for troubleshooting and ideation at work and home.)

Image 1: Chat screen with lead developer Mark Thomas (at U of U Health) about his experience with new generative AI tools.
For those who have used it, but perhaps have not incorporated it into their own processes more regularly, I added the answer “as needed”. (It’s hard to work something into your workflow that you don’t regularly need :D.)
Prediction: I believe that a year from now, our answers to this poll will not be significantly different. I do think, however, that we will have better incorporated gen AI into our processes.
AI Use at U of U Health
The next question focused on AI at our institution. The question about where AI is being used allowed users to add any reply. There were three main categories into which the answers could be classed:
- Generative AI tool use specifically
- Institution services/department references (some more specific than others)
- I dunno’ responses
With 34 responses, here are the cited uses of AI that our respondents are aware of at U of U Health:
Generative AI
- Photoshop (for use in image editing)
- Utah Magazine (not sure how but with development–I think giving/donor development)
- Video editing and advertising
- Idea generation
- Epic (the electronic medical record system used by the institution)
- Writing/rewriting/refining
- Emails
- Interview outlines (rough drafts)
- Podcast descriptions (rough drafts)
- Meeting notes
- Letters of recommendation
- Social media posts
- Article or book summarization for learning purposes
- Stock image/illustration search
- Troubleshooting (I assume in context of web development)
Institution Services/Departments
- Radiology services/department image reading
- Biomedical Informatics department
- Identifying “critically ill newborns who are best candidates for rapid whole genome sequencing and using that to guide care for these newborns. We are doing this work in collaboration with Rady Children’s (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36927505/).”
- Lung cancer predictive screening: “We have used predictive models on lung cancer risk to help improve screening for lung cancer, the leading cause of cancer deaths. We have increased the odds of screening for lung cancer at U of U Health by 5-fold (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37142092/).”
Obviously, if a respondent worked with a specific program/department/study using an AI tool, they were able to identify more specific use cases.
Hypothesis: Many entities/programs are experimenting with the use of AI at U of U Health and this will continue for the next several years.
Time/Money Savings
The next question focused on savings in time and money. I did not structure the question here so that a respondent could choose multiple answers. Fortunately, I did add an “other” option, in which the respondents let me know of this misstep.
Due to that, I have restructured the original data-generated poll graph to better categorize all answers:
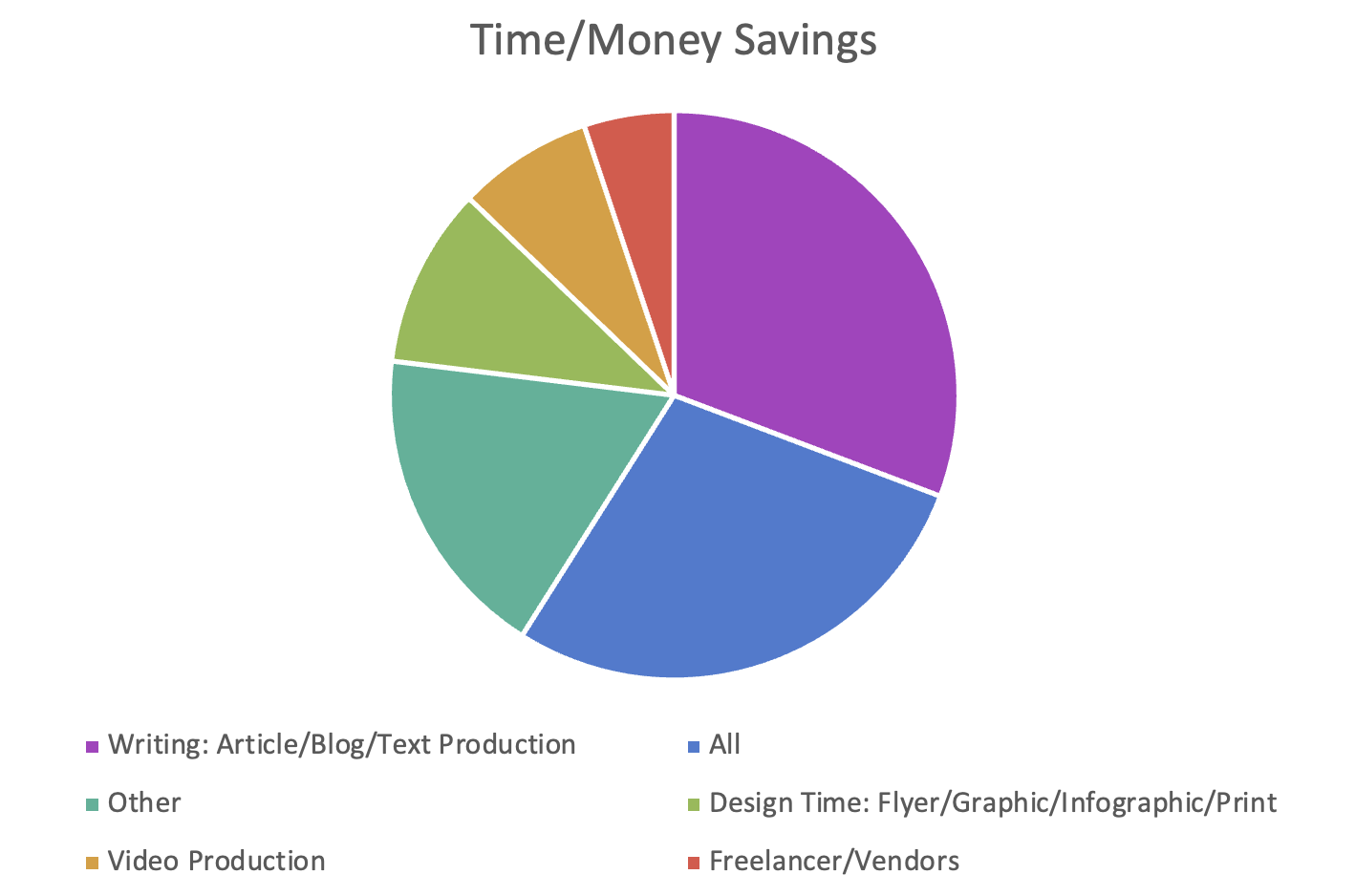
Fig 3: Answer categories (and number of answers) of potential time or money saving uses.
Please note that the answer “Other” consists of the following:
Other
- Information Consolidation
- Research
- Brainstorming
- Email Responses
- Social Promotion
- Longer Term Use
- Audio
Greatest Potential Misuses
Question 5 asked users to choose (multiple choice) what they thought the greatest potential misuse of AI could be.
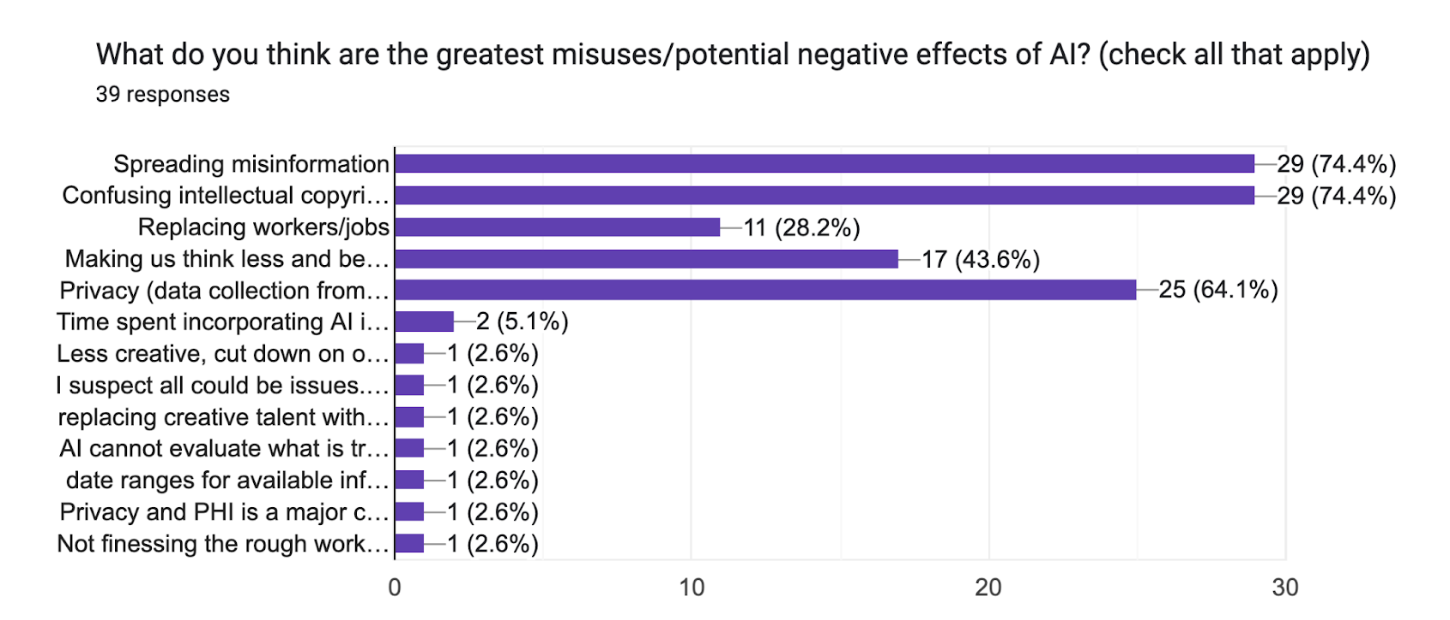
Fig 4: Line chart showing most selected answers regarding the greatest potential misuses or negative effects of AI.
Tied as the most selected were these two answers:
- Spreading misinformation
- Confusing intellectual copyright
Data collection and privacy ranked as the third potential highest area of misuse.
I also inserted a more qualitative, open-answer question asking users how they felt about AI and the future of work. Many thought it was great but has unachieved potential. Some worried about keeping up with changes in AI tools and applying them to their works.
Summary: Most respondents worried less, however, about whether we should be using these tools and more about regulation, quality of work produced, and costs.
Identifying AI Use Elsewhere
For Question 7, I wanted to see if respondents could or had identified the use of AI by other entities. Out of the 30 respondents to this question, some answers were pretty generic or just no/don’t know.
Here are some of the more in-depth answers (categorized for easier analysis).
Obvious AI Use



(How can we joint this group?)

Less Obvious & Generalized AI Use/Hearsay


Summary: These answers confirmed what we all see, or don’t see: Everyone is trying out the tool or has been using it and we may or may not be able to guess. (Unless you are as good as the person who noticed that some newsletters have no soul…I feel you.)
Best Uses for AI
Next question: What are the best uses for AI? I’ve put these answers in a graph by categorization (by use case–and note that some respondent answers identified multiple uses).
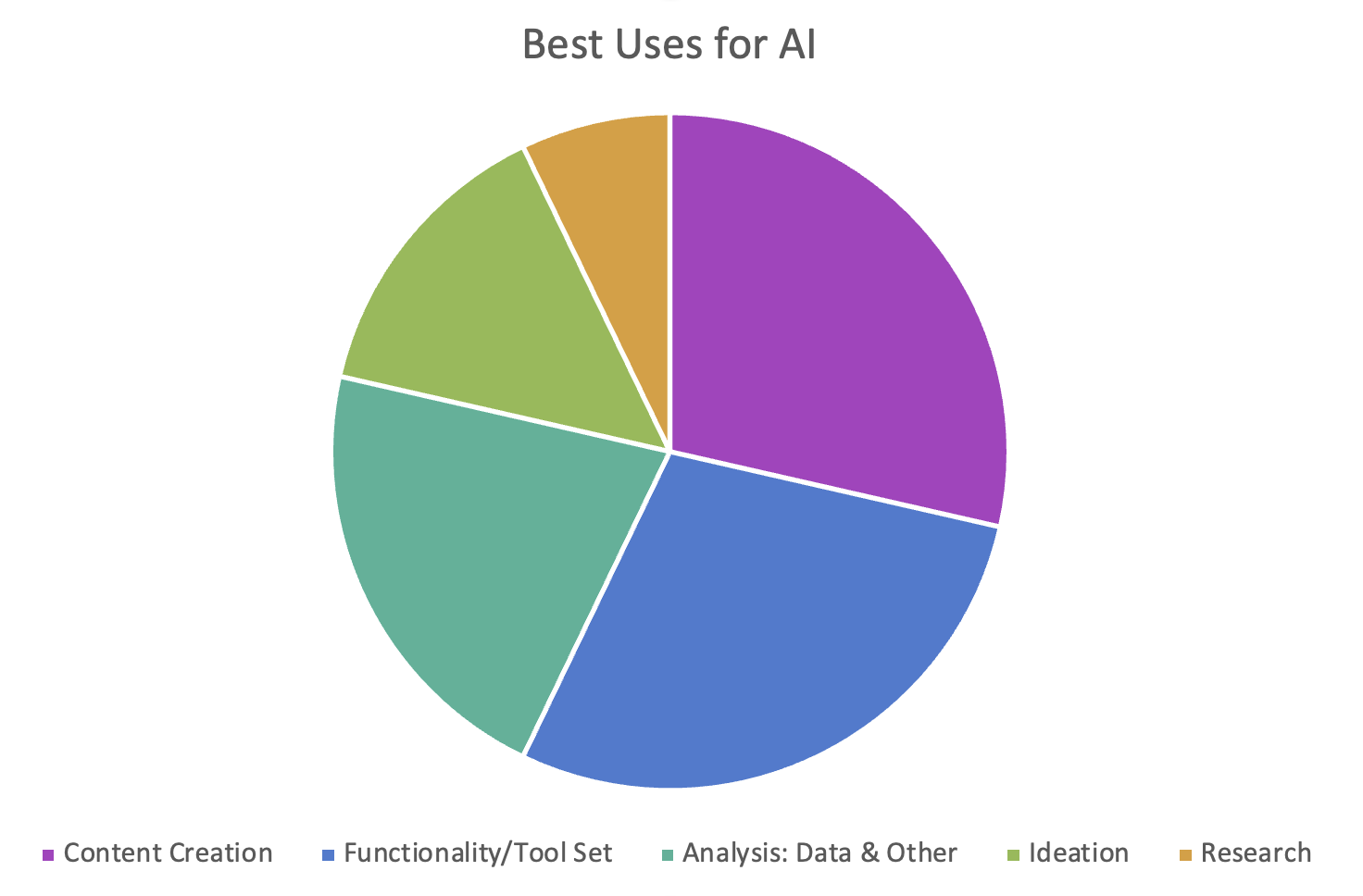
Fig 5: Answer categories (and number of answers) around best uses of AI.
Here is the full list of responses (summarized):
Research
- Research (including time saving)
- Social media influencer/hashtag research
- Topic exploration
Ideation
- Brainstorming
- Teacher/Intern/Sounding board
- Higher-level thinking (INTRIGUING)
- Design
Content Creation
- Outlines
- Thesaurus
- Repurposing
- Headlines
- Captioning
- Persona/brand extension (specific example: deceased artist covers–INTRIGUING OR DISTURBING?)
- Photos
- Illustrations
Analysis: Data & Other
- Analysis
- User sentiment
- Arguments/presentations
- Error reductions in the analysis of large datasets
- Large text set analysis
- QA (quality assessment)
- Summarization
- Information display
Functionality/Toolset
- Conduct repetitive tasks
- Enhanced tools
- Chatbots
- Enhance/complete
- Speed up tasks
- Note-taking
- Copyediting
- Productivity
Summary: These responses, I believe, confirm our own experiences. (Since we all could potentially be “experts” in AI use.)
Worst Uses for AI
For this question we had 34 respondents. Again note that some respondent answers identified multiple uses. See the answers, again categorized and then the full list:
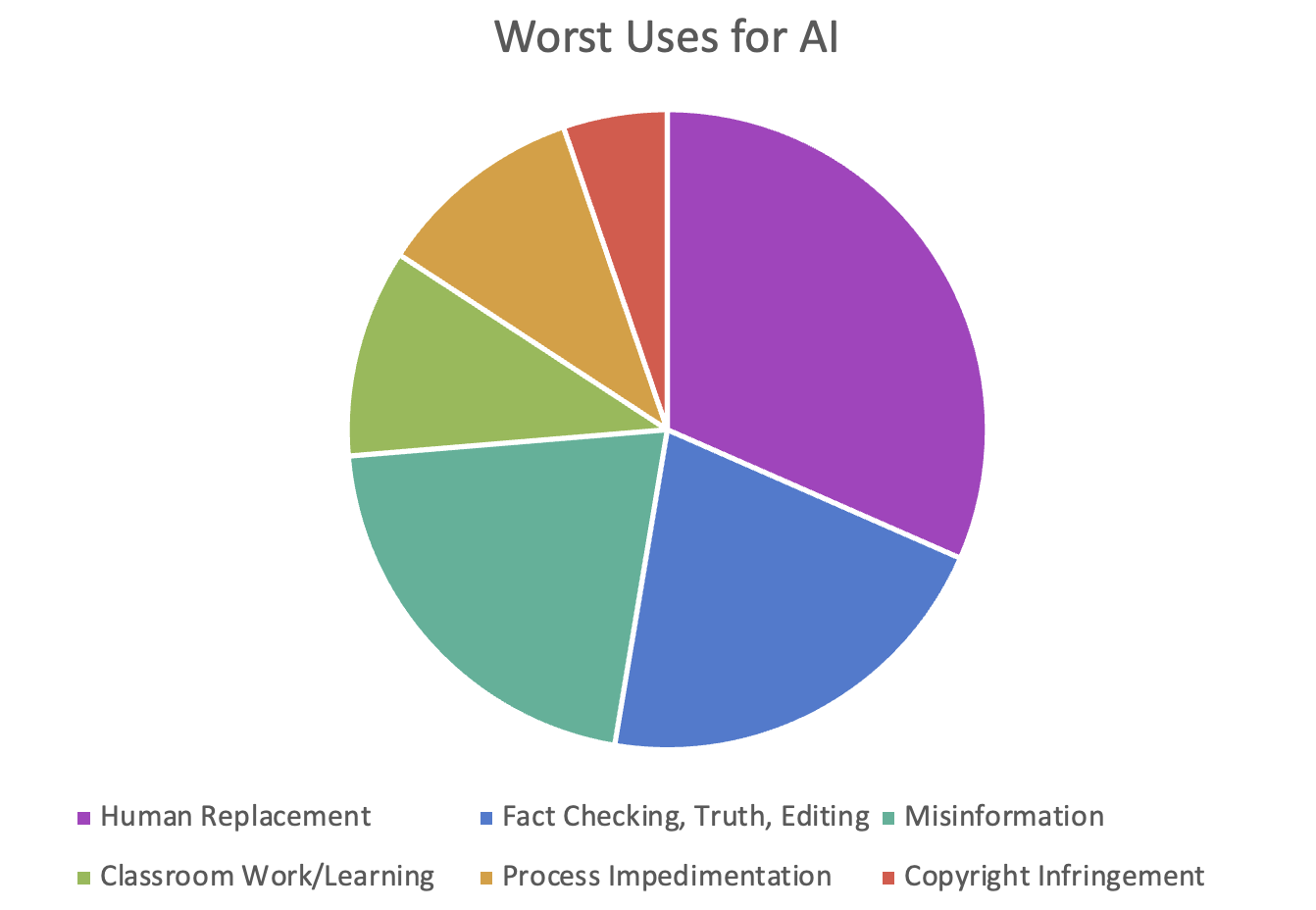
Fig 6: Answer categories (and number of answers) around worst uses of AI.
Fact-Checking, Truth, and Editing
- Use of AI as the final source of truth
- Data verification/fact checking
- Final drafts
- Fake references
Classroom Work/Learning
- Student use for classroom work
- Inhibits creativity or skills
Process Impedimentation
- Continual rewrites when you aren’t getting the rewrites you want from prompts
- As the only tool
Misinformation
- Misleading content
- Use on news and government platforms
- Intentional misinformation
- Provider notes
Replacing the Hooomans
- Replacing human thoughts and ideas
- Replacing human-created work with lower quality work
- Making bread–my favorite answer! And companies in San Francisco at least are experimenting with replacing humans in food service.
- Replacing jobs
- Takeover of content production
Copyright Infringement
- Generating content without thought for copyright
Respondents
The final question, again not required, asked for the main identity of each respondent primarily so we could see what disciplines were represented in our survey.
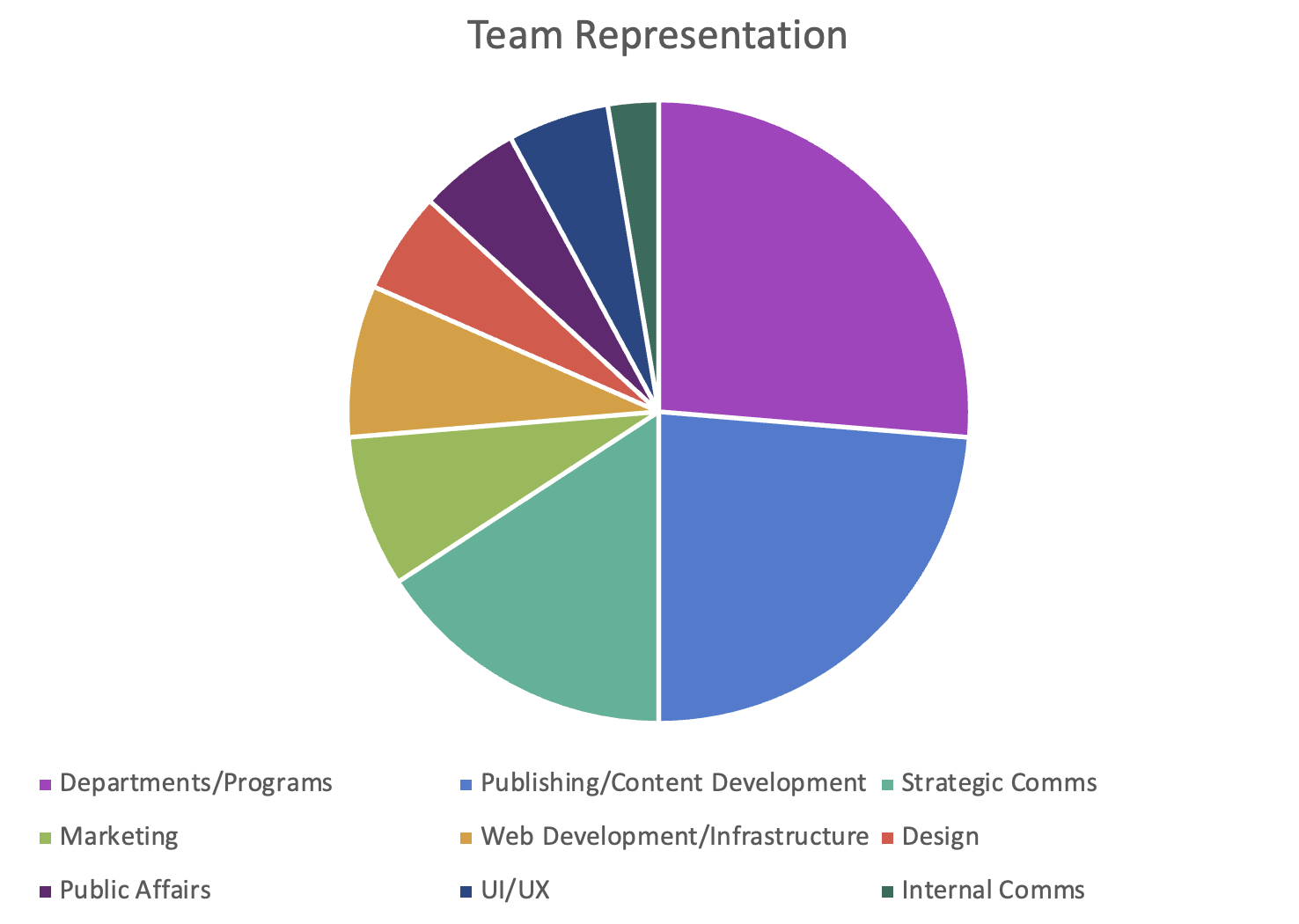
Fig 7: Respondents classified by department, program, or entity.
Note that Departments/Programs include the following:
- OPMO: Project Management Office
- Service Line Director (Dermatology)
- IT
- UUMG: University of Utah Medical Group
Thank you to all those who participated. Your input was greatly appreciated!!
The Whole Enchilada
So, that’s quite a lot to digest.
If I were to say one thing that you should remember, it would be this: be cautious about the tools you use and what data is going where.
Note that any information you enter that is proprietary for your work, such as meeting summaries or email rough drafts, is used by open AI (such as ChatGPT) to continue training model.^
If you opt for a paid subscription model (which we all will have to eventually) and want to create something proprietary, consider the work it will take to customize this and if you might potentially switch tools (time investment vs. time the tool saves/contributes value).
In the end, nothing has really changed. It still goes back to time, money, and effort and how to make the best of the tools we have at hand.
Originally published on Pulse, the U of U Health Intranet, Dec 14, 2023
*Editor-at-large is a publishing title used in print, now often digital, publications. It refers specifically to an editor who writes on no one specific topic of specialty, but reviews trends and industry shifts.
My favorite editor-at-large of all time was ALS or Andre Leon Talley for the uninitiated. Both his perspective, as a Black American in fashion, and his self-deprecating take on fashion were unique and fantabulous.
^Source: Weighing the Open-Source, Hybrid Option for Adopting Generative AI, Harvard Business Review






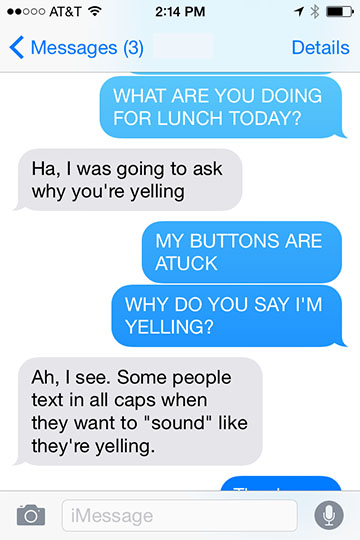 TEXT MESSAGING OR EMAILING IN ALL CAPS WITH YOUR CHILDREN/FRIENDS/CO-WORKERS, EVEN IF YOUR KEYS GET STUCK—THEY WILL THINK YOU ARE SHOUTING AT THEM.
TEXT MESSAGING OR EMAILING IN ALL CAPS WITH YOUR CHILDREN/FRIENDS/CO-WORKERS, EVEN IF YOUR KEYS GET STUCK—THEY WILL THINK YOU ARE SHOUTING AT THEM.