These thought threads are not going to be speculation on a dystopian future (if you haven’t read your sci-fi, time to get an AI summary of the classics) but rather a questioning. Like the quickening (the acceleration of the pace of change), the rate at which I question what happens around me is accelerating.
Does this generally happen as one achieves more life time or is it a function of our times? (—>has also thought every author/artist ever…) As our civilization fractures and re-organizes around the fourth industrial revolution, I find I’m questioning almost everything.
5 Question-Based Thought Threads Around AI
We’re all working towards that magic sauce that is the perfect consistency of workflow zhuzh and time-saving sauce. They claim AI will fix it. But I have to wonder…
1. Why do we need more tech?
Is it a function of getting older that we don’t want to change? Or rather is it that we don’t want the things that were once easy to change? Or is it just that I don’t need more to do?
As our bodies become more difficult to manage and new experiences become fewer and farther between, I have to ask what is progress? And why is progress often measured as tech? WHY does tech have such an impact on our lives and SHOULD it?
I know, I know. I’m joining a curmudgeons-R-us group.
2. How much time do I have to spend with AI? (*Spoiler* time/relationship zhuzhing from complicated to weekly…)
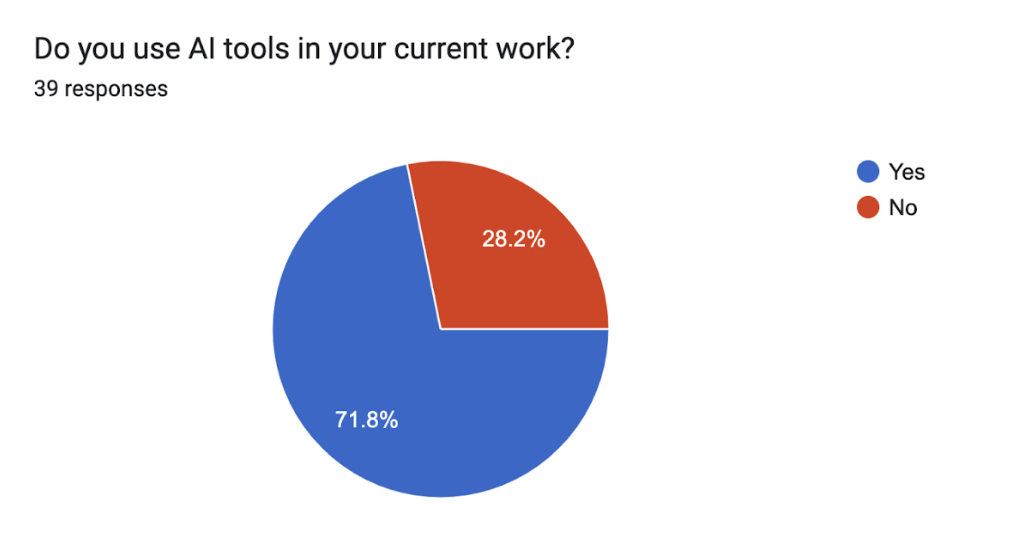
SOME of us use genAI quite a bit. We actually occasionally get told we must take a break (cough ChatGPT cough) because we have asked so many questions (no–not me doing this).
But how much time do we need to regularly spend with AI? (Guess what–you already spend more time than you may want to!)
Almost all tech tools we use today are driven by predictive modeling, LLMS (large language models), or even neural networks (the largest energy price tag). Not only that, tools that we have used previously have, whether we were aware or not, used AI.
I used an app to generate interesting images for projects long, long before I even wondered how that tool generated what I selected (think image filters).
But exactly how much time must I devote to this practice?
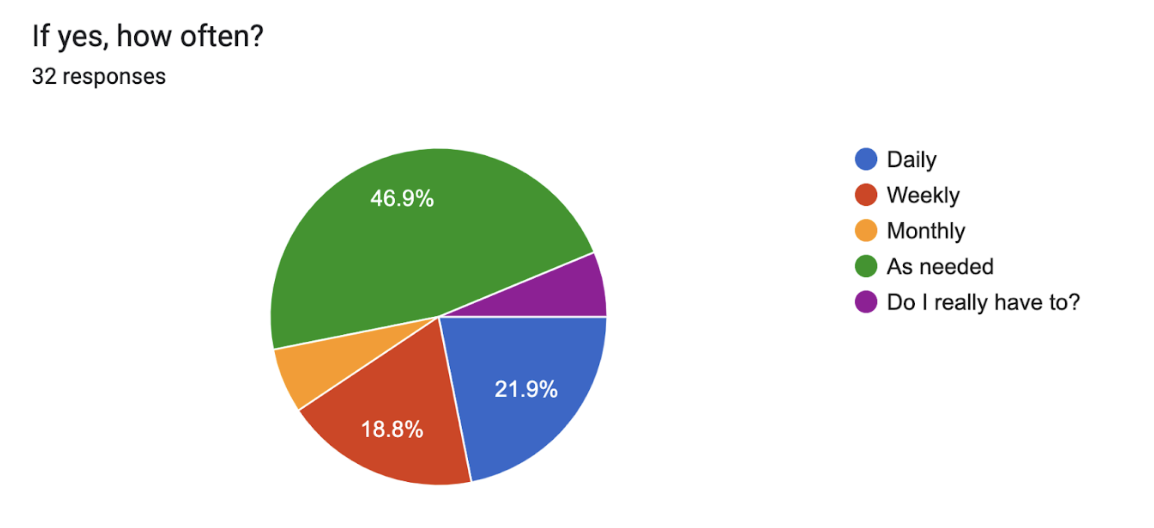
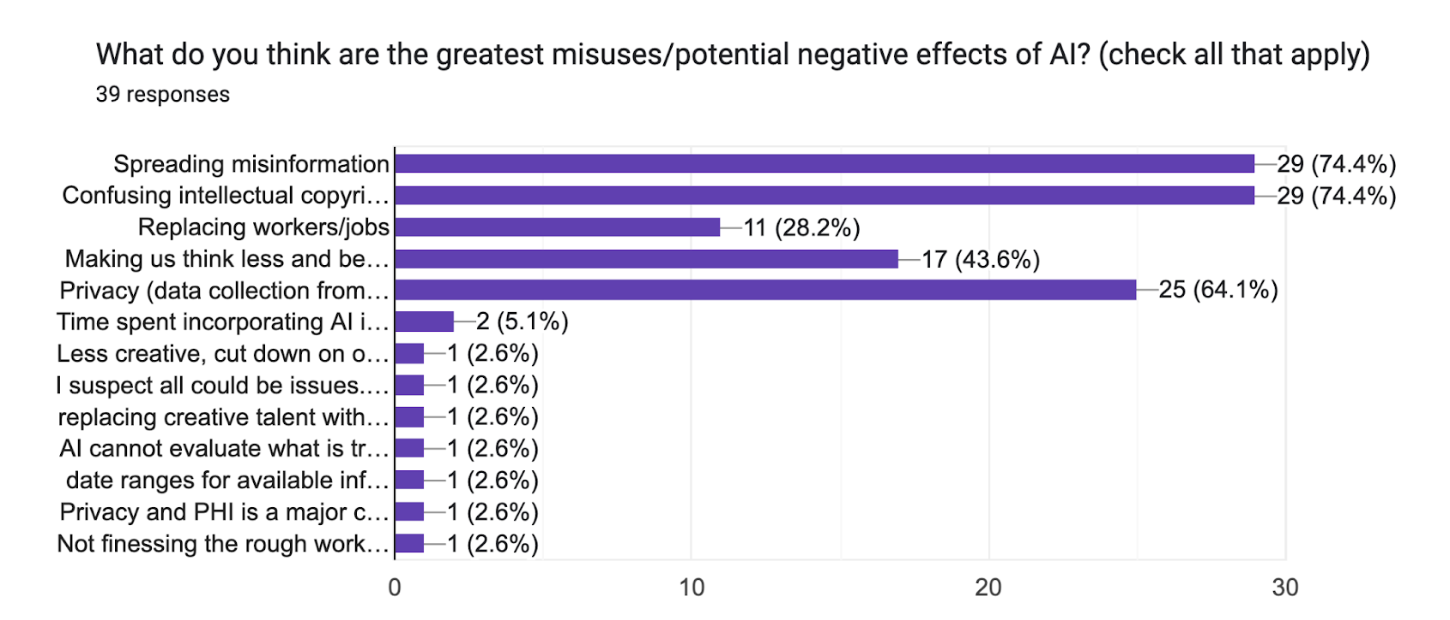
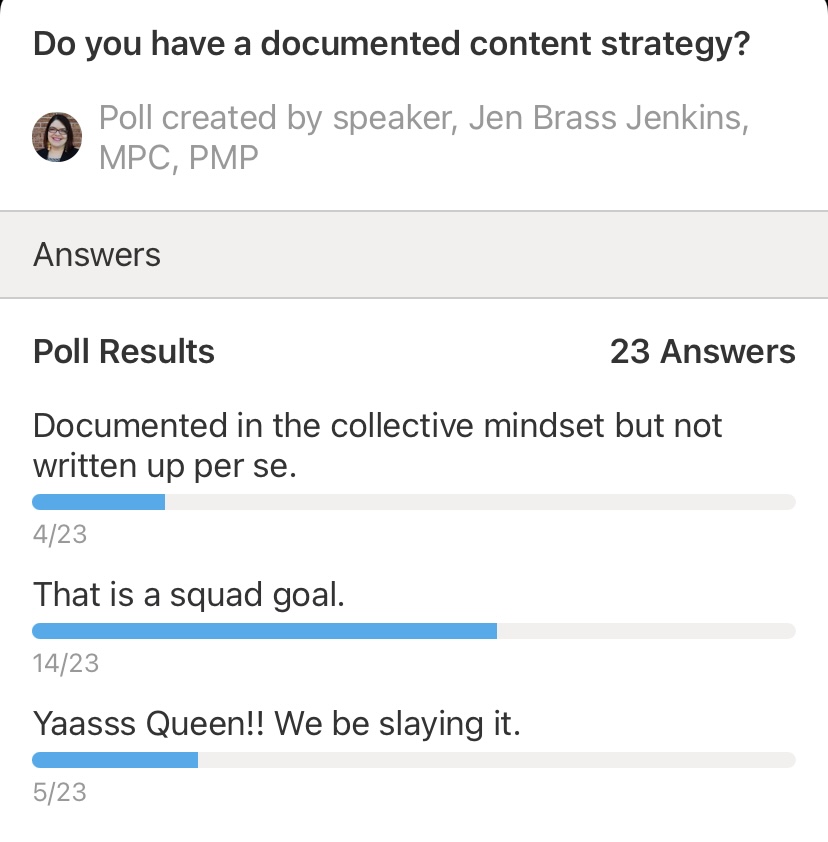
Since I love to conduct polls, I’ve got some data (wheh-hoo!) for you from the annual SEO Summit (now SEO/GEO Summit), that I hold for the MarCom department. I found that this was how often my colleagues used genAI:
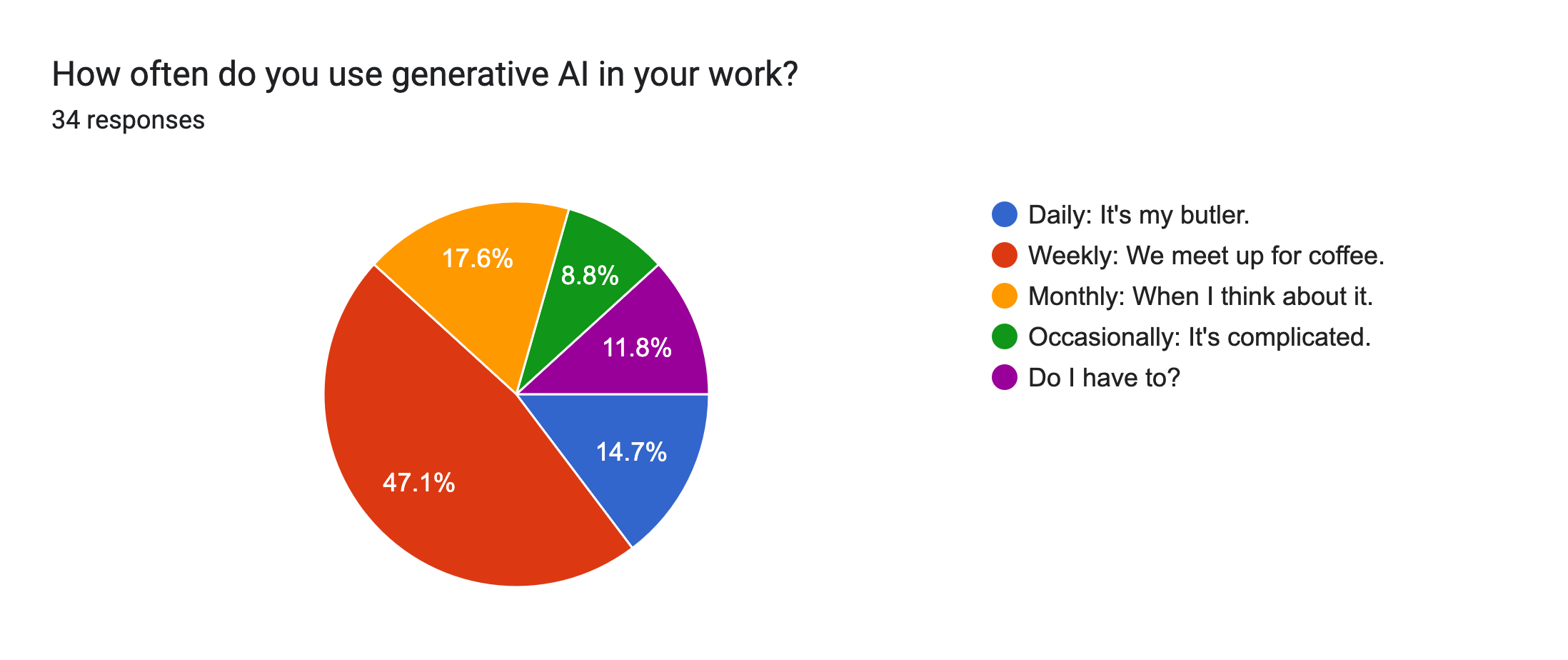
Looking at this pie chart, you can see that 47% said they actively use it once a week (that number is probably inflated to be honest) and that 15% use it daily. (Note: few of the web developers participated in this survey and none self-identified.)
If you ask how often I spend with genAI, the answer is complicated. Honestly, my usage is increasing just in the last few weeks because SEO tools I use almost daily have just released some integrated AI features. (It must be exclaimed!!!!)
And I need illustrations for things like this blog, so I’m now using genAI on a more frequent basis. My predictive gut says I’ll be using it weekly from now moving forward. That’s kind of a shocker!
Most people I talk to really enjoy the use of AI for their personal lives. They use it for compiling grocery lists and recipes, brainstorming and planning trips, and now–I’m sure–shopping. (GPT is releasing a shopping feature in their genAI tool.)
3. How healthy is it to depend on AI?
Did any of y’all read the recent article in Harvard Business Review on uses of AI? (I flocking love HBR.) They polled how people used genAI a year ago vs. how they are using it now.
I found it very insightful because the top uses changed from ideation to therapy and life organization. I do believe AI can be very useful for people who need to ruminate or just to share their thoughts with someone.
Here’s where we get into the gray space though. How much do you want the AI to remember about you? How much do we want the company that owns an AI to profit off of us?
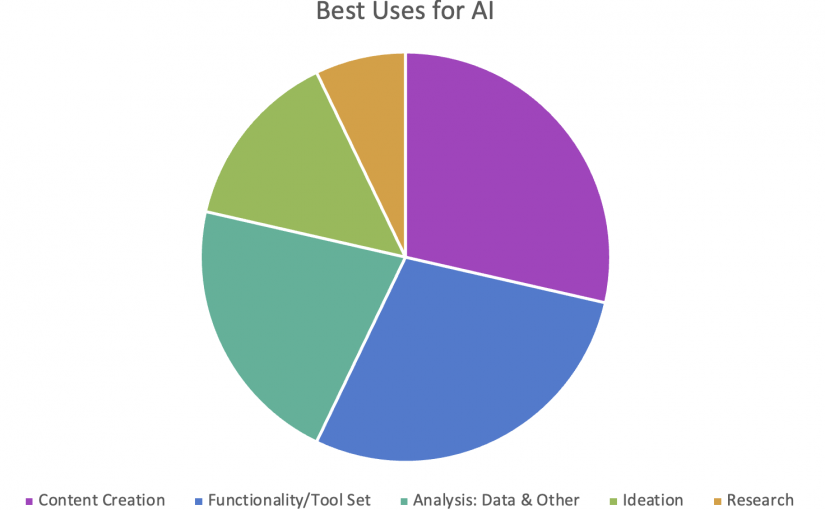
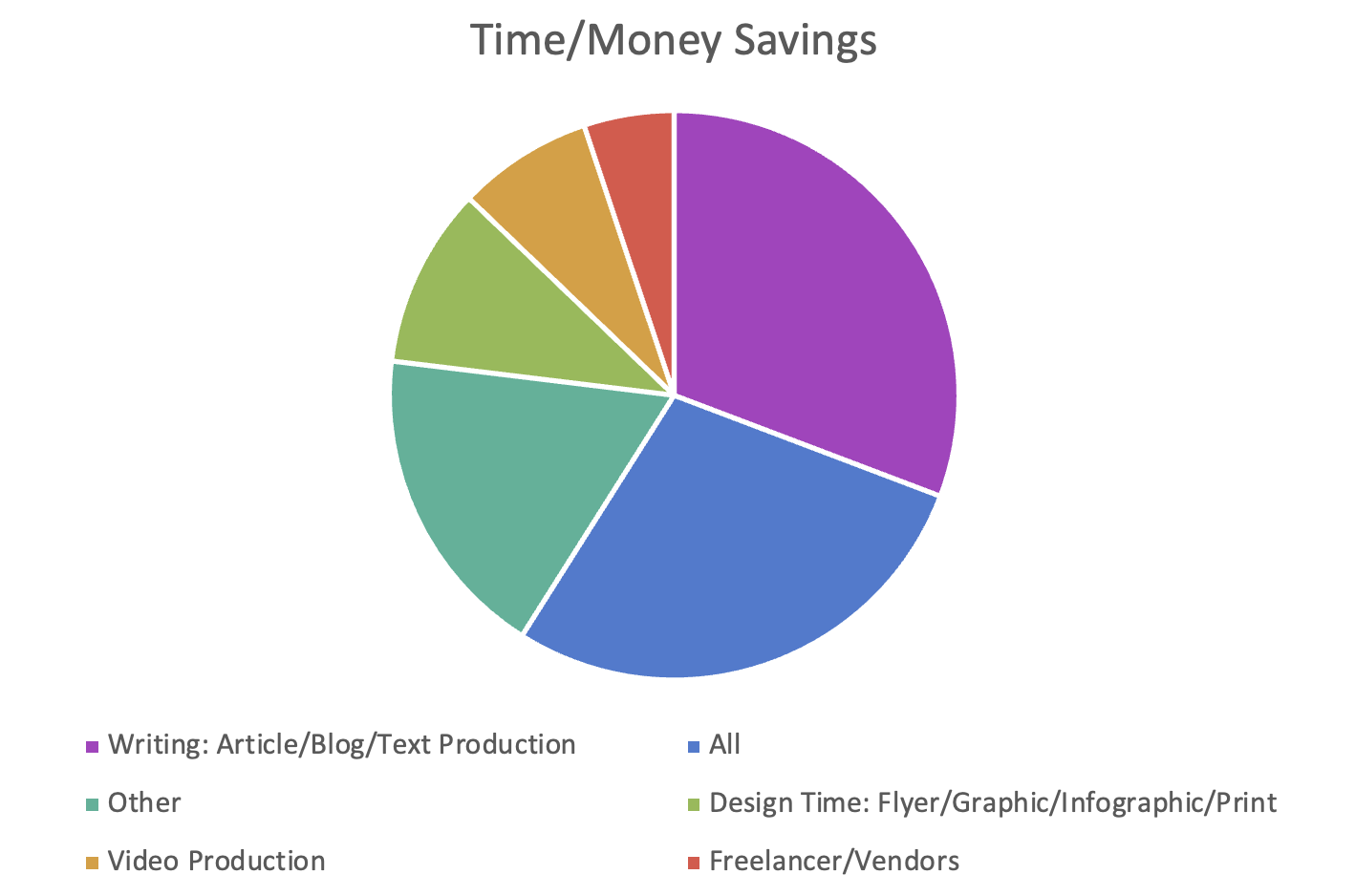
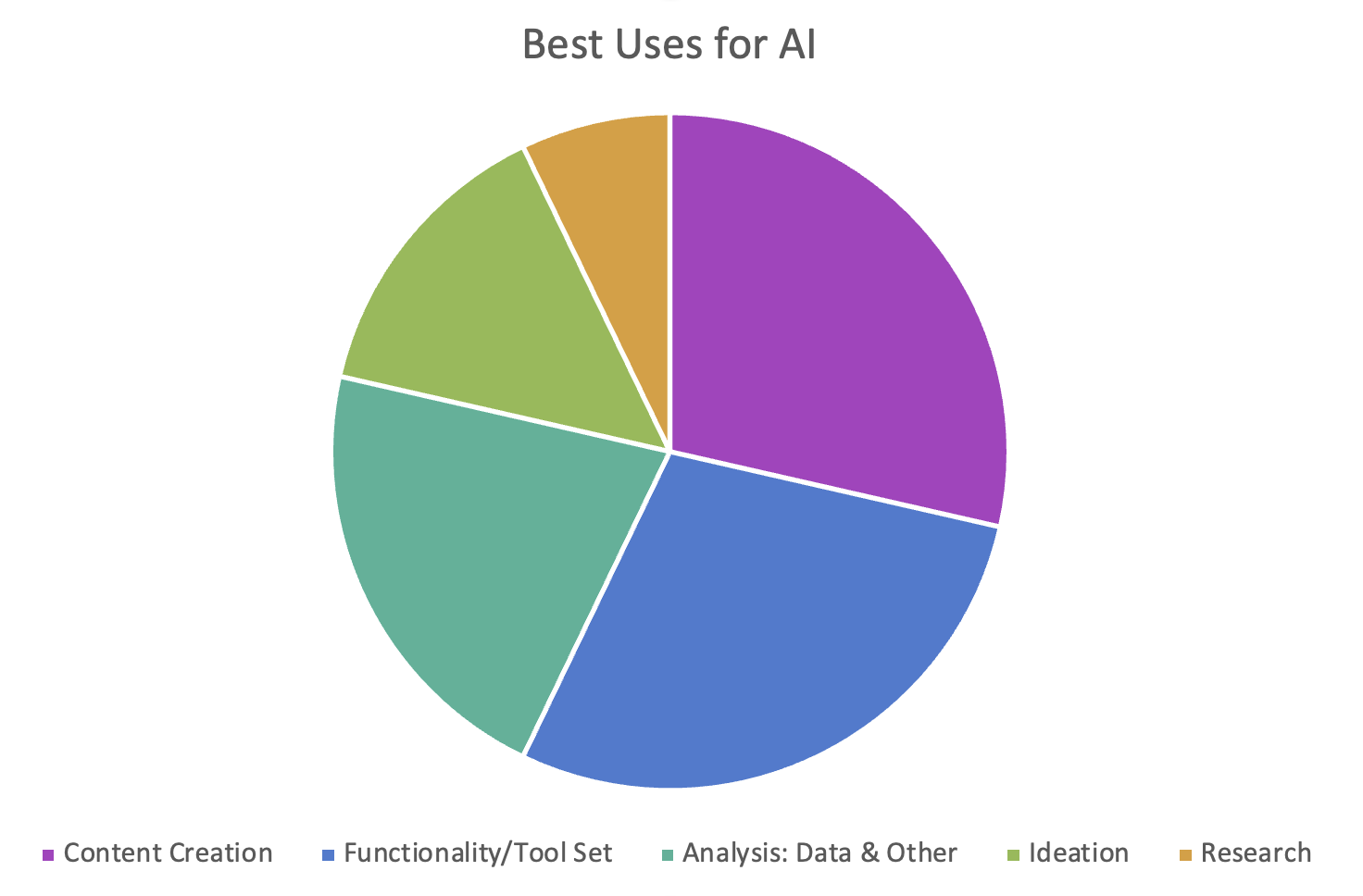
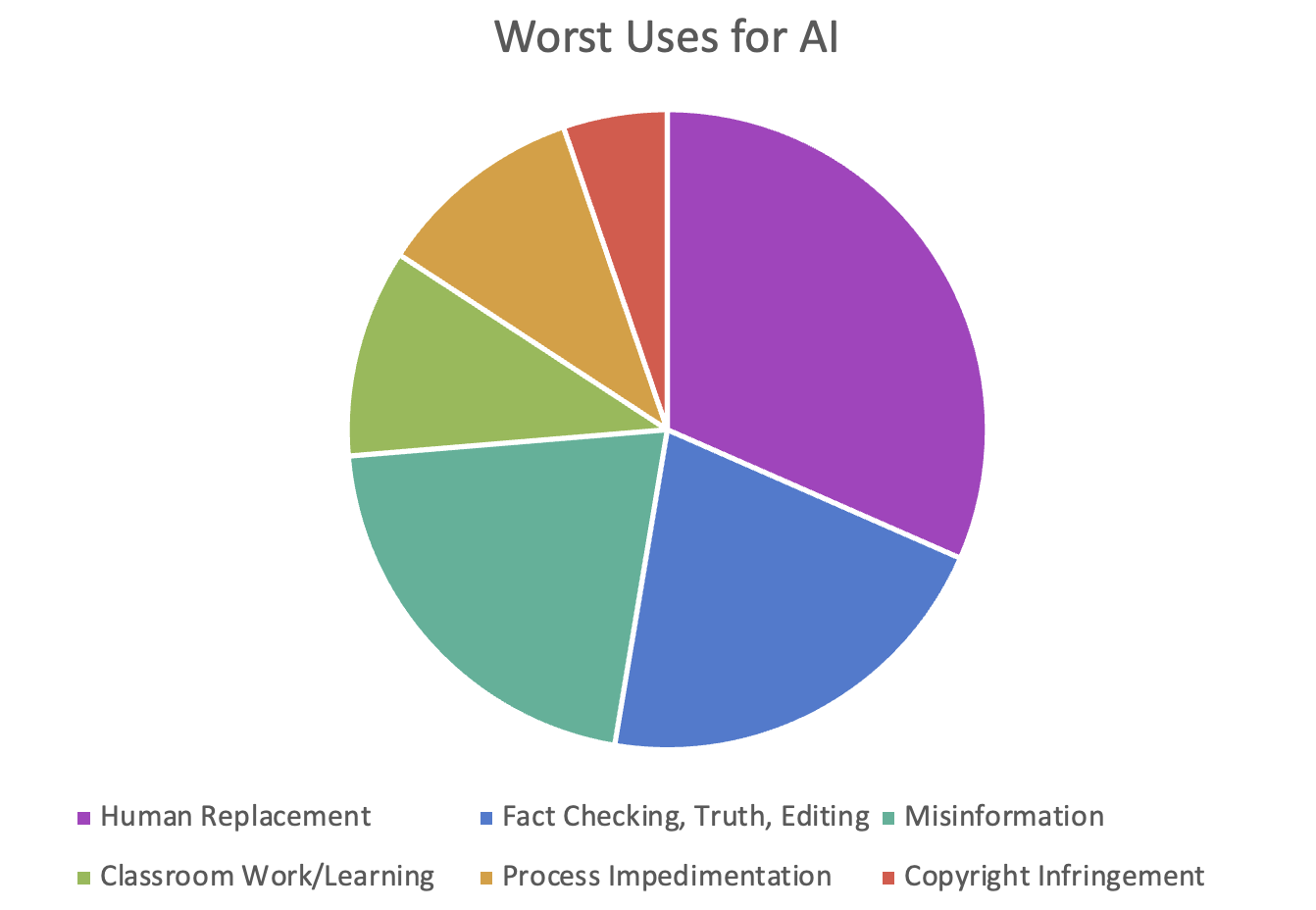
On a more positive note, I also did conduct a poll in my own department about how colleagues used genAI, and here are the results:

I have to say that in my own experimentation, here are my favorite uses to date:
- Summarization of large sets of written material
- Persona generation and analysis
- Gap analysis on webpages or other content types
- SEO/GEO (Search engine optimization or now generative engine optimization)
Turns out genAI does have some uses! Whether or not those uses are healthy, I will leave up to you to judge. I am not a fan of its use for p*rn, but that ship sailed with the interwebz in general.
4. Who watches the watcher/AI?
In all the best dystopian novels (again–YOU SHOULD READ THE IMPORTANT SCI-FI TEXTS), AI is overseen by powerful entities or even oversees itself. These entities are depicted as either domineering or overseeing. Whether they watch overtly or covertly, the point seems to be that the function of intelligence is to watch and potentially dominate.
Why?
Is the function of the watcher culturally appointed? Or is it the way our civilization has been structured? What is the role of intelligence?
5. And finally, why didn’t they ask me?
If you are a consumer, which is everyone, and self-aware, which is a much smaller portion, you may find yourself thinking, why, in the name of all that is holy, did they not ask me? I would LOVE to give some input into HOW AI is used or even WHAT it is used for.
They say AI is about reducing repetitive processes. I could use help with these:
- Fixing broken links
- Scheduling meetings
- Communicating with stakeholders
- Creating cross-departmental reporting
- Doing laundry
- Doing dishes
- Cleaning the litter boxes
Over the last 2.5 years, I have waited for AI to achieve these results, but guess what, these repetitive processes I would love to do without will probably never be replaced. Why? Because of contextual and very human reasons.
And if you have heard me complain about all this before, that means it’s ‘cause these are constant needs resulting in repetitive processes. I know. Go figure.
But it does bring me back to the question (of questions) at hand: When will technology address the problems that I actually have?
Zhuzh the Sauce
So, as you work on zhuzhing the sauce, I’d suggest you go a bit meta. When you are on brain default setting (your thought trains turning into fluffy cloud bunnies hopping here and there), try pointing them towards intelligence, products, problems, and special sauces.
Give yourself room to question. I guess that means we may be joining the quickening…
BONUS: What are the important sci-fi texts? (Since you asked…)
I just asked CoPilot (Bing genAI tool) to pull me a list of more important sci-fi texts over the last 100 years.
****
- I, Robot by Isaac Asimov (1950): This collection of short stories introduced the famous Three Laws of Robotics and explored ethical dilemmas and human-robot relationships [1].
- Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep? by Philip K. Dick (1968): This novel, which inspired the film Blade Runner, delves into themes of machine consciousness and empathy, questioning what it means to be human [1].
- 2001: A Space Odyssey by Arthur C. Clarke (1968): Featuring the iconic HAL 9000, this story examines AI reliability and the potential dangers of advanced AI [1].
- Neuromancer by William Gibson (1984): A cyberpunk classic that introduced the concept of cyberspace and AI transcendence, blurring the lines between human and machine minds [1].
- The Diamond Age by Neal Stephenson (1995): This novel explores AI as an educational tool, presenting a future where interactive, AI-powered books shape young minds [1].
- Klara and the Sun by Kazuo Ishiguro (2021): Focusing on an Artificial Friend named Klara, this novel explores themes of existence, spirituality, and the impact of AI on human relationships [2].
These works (and others) have shaped our understanding of AI and its potential impact on society. Do any of these titles stand out to you?
References
[1] 20 Top Sci-Fi Novels About AI: Origins and Controversies
[2] 20 Must-Read Sci-Fi Novels about AI – BOOK RIOT
*****
Okay, I think I forgot that even the thought of AI may not have existed in 1925…
Have you read any of these? And what did you think? I’ve read almost none of them (and yet I still have Thoughts about AI), and there is one, IMO, very important exclusion: The Murderbot Diaries by Martha Wells.
While some have dismissed these amazing novellas and books about Murderbot the AI construct, as mere plot-driven pleasure-inducing fantasies, I find them much more insightful. If you are a semi-self-aware questioner in the quickening that is.
Have you spotted the questions Murderbot explores? Lemme’ know.
^Polling happened in Mar 2025. There were 34 respondents out of a 10-question survey.
^^Teaser image AI generated; fry sauce a Utah thing